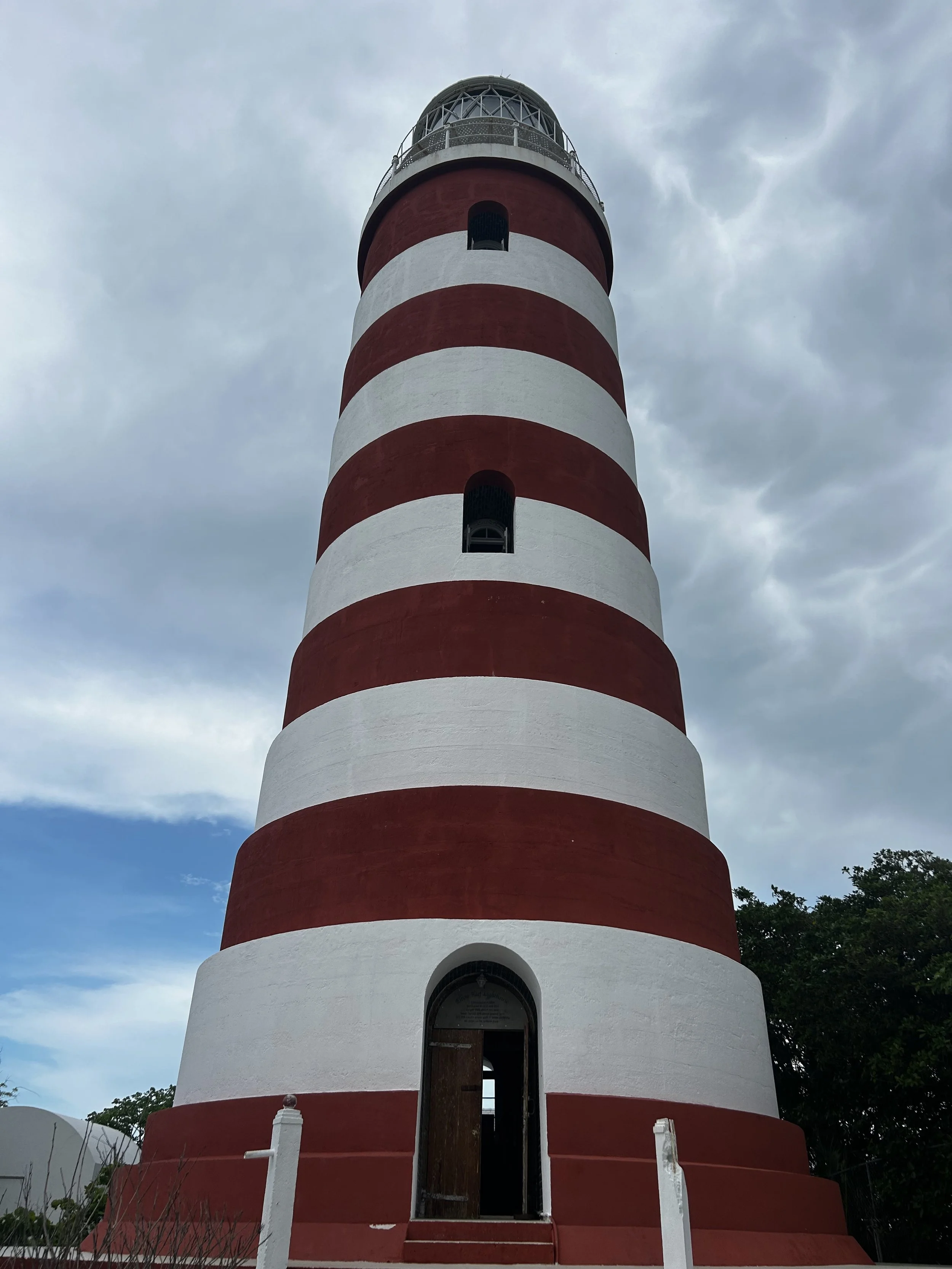
Constructed by the British Imperial Lighthouse Service, the Elbow Reef Lighthouse was one of 11 manned lightstations built between 1836 and 1887 to curb shipwrecks on the Bahamas' perilous reefs.
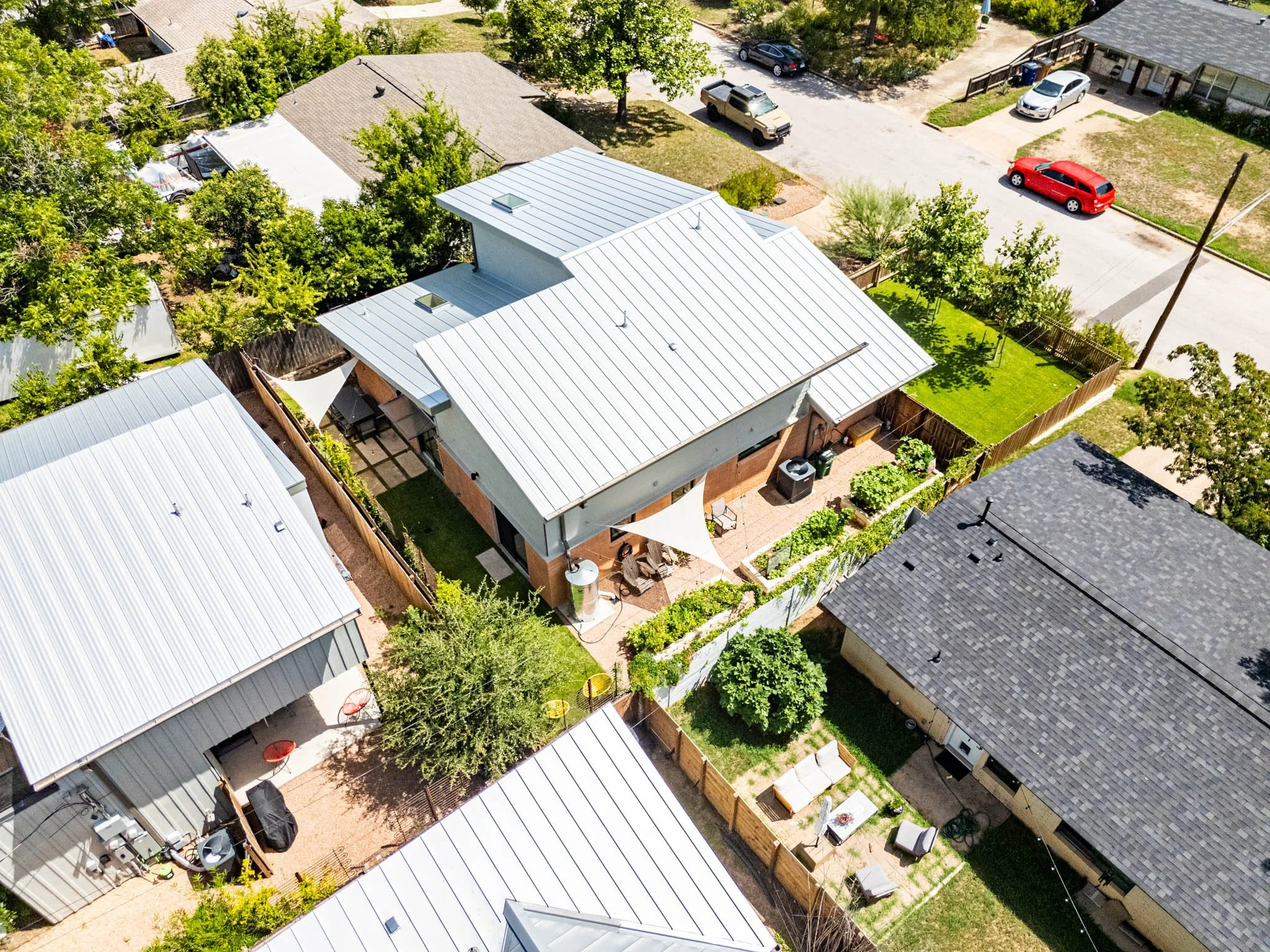
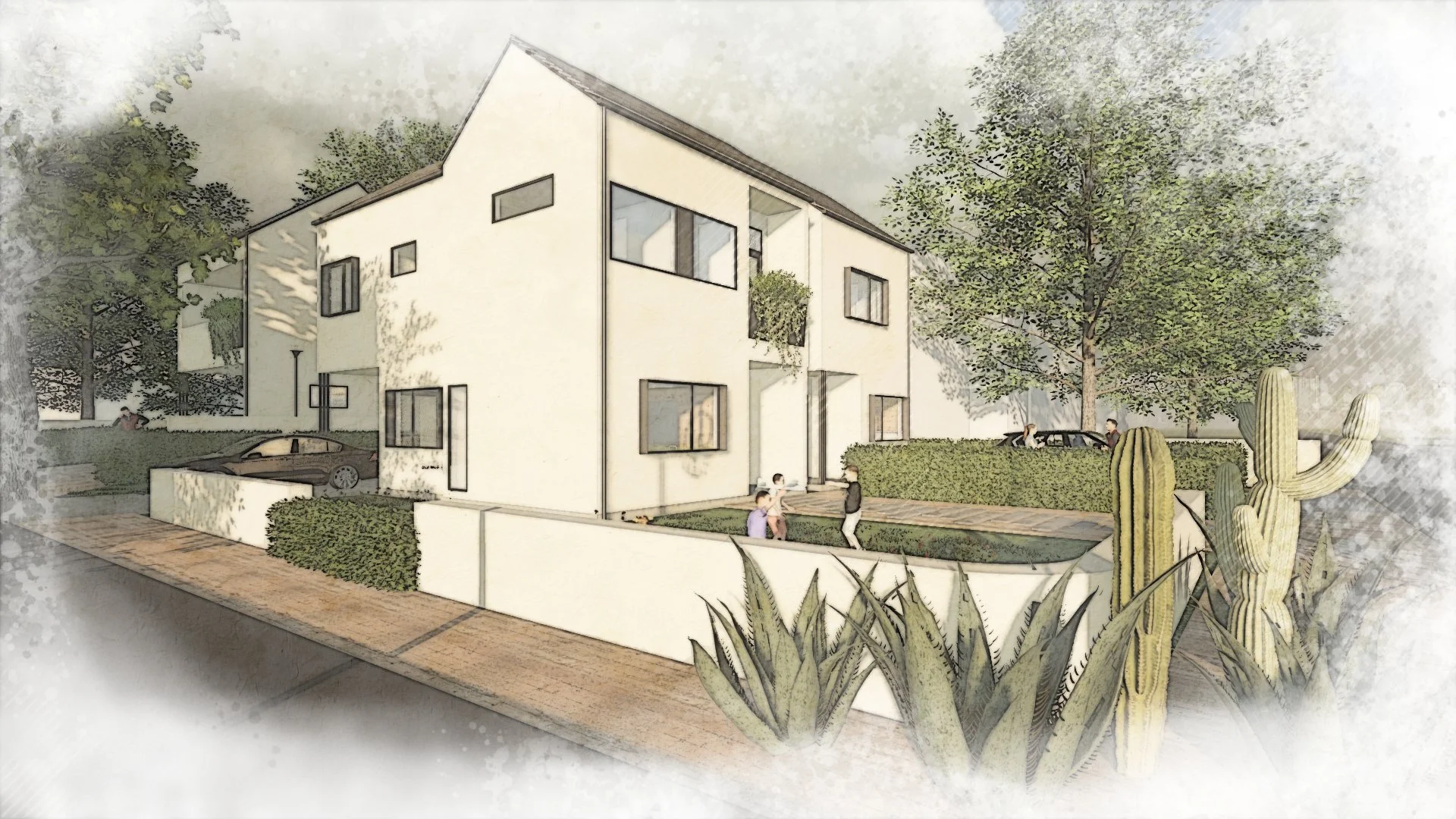
Missing middle housing refers to a range of housing types that bridge the gap between single-family homes and large apartment complexes. These include duplexes, triplexes, fourplexes, townhouses, and accessory dwelling units (ADUs). Missing middle housing provides more density than single-family homes but falls short of the high-density urban developments that dominate Austin’s skyline.
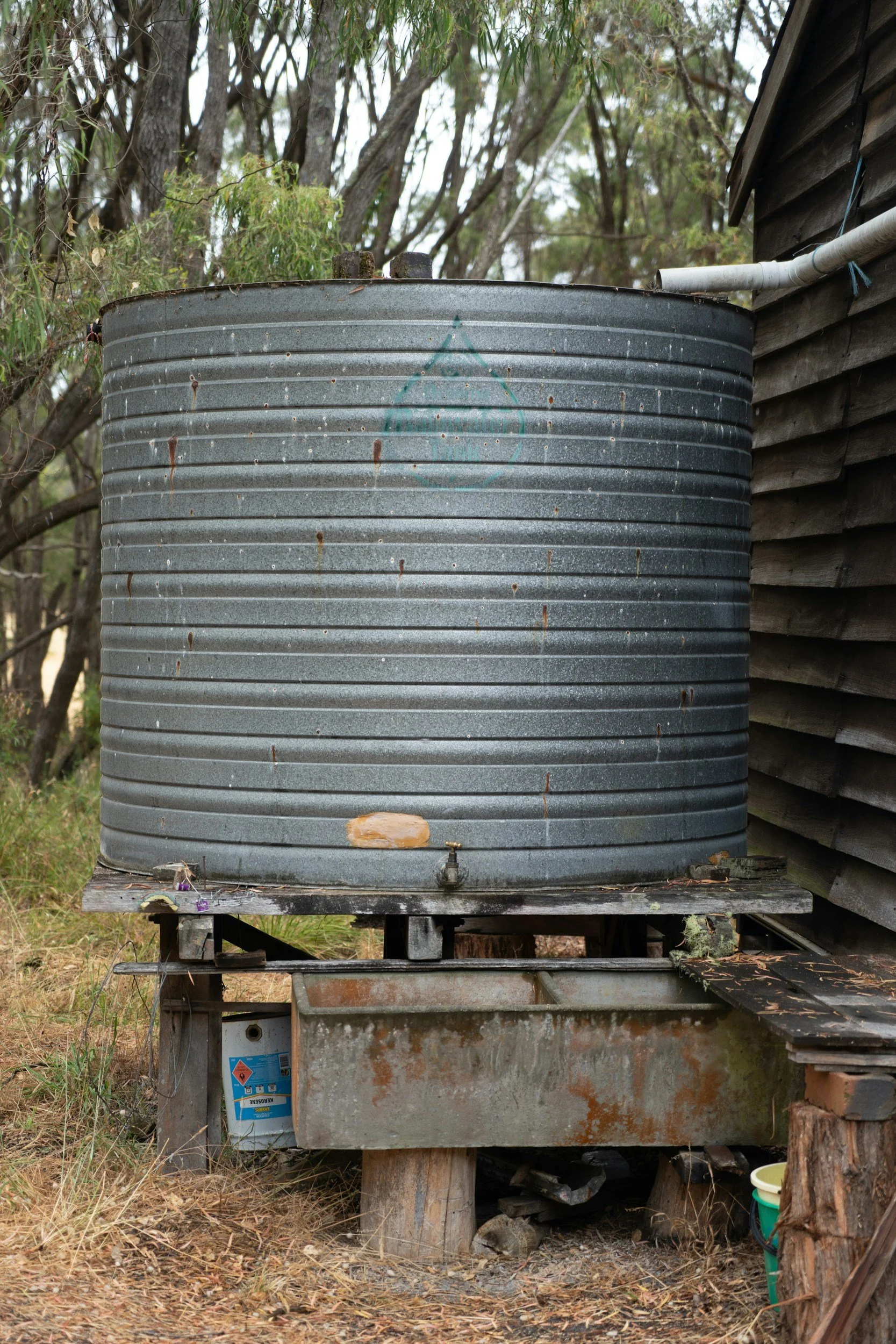
Rainwater collection has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its sustainability and environmental benefits. It helps to conserve water resources and reduce the demand for treated water, which can be expensive and energy-intensive to produce. In addition, rainwater collection can help to reduce the risk of flooding and erosion by capturing and diverting rainwater from paved surfaces.
Suburban development in the United States refers to the expansion of residential, commercial, and industrial development on the outskirts of urban areas. Suburban development typically features low-density, automobile-oriented development patterns, including single-family homes, strip malls, and office parks.
New Urbanism is a planning and development approach that seeks to create walkable, mixed-use communities with a variety of housing options, transportation alternatives, and commercial and civic amenities in close proximity. The philosophy behind New Urbanism is that neighborhoods should be designed to foster social interaction, community engagement, and a sense of place.
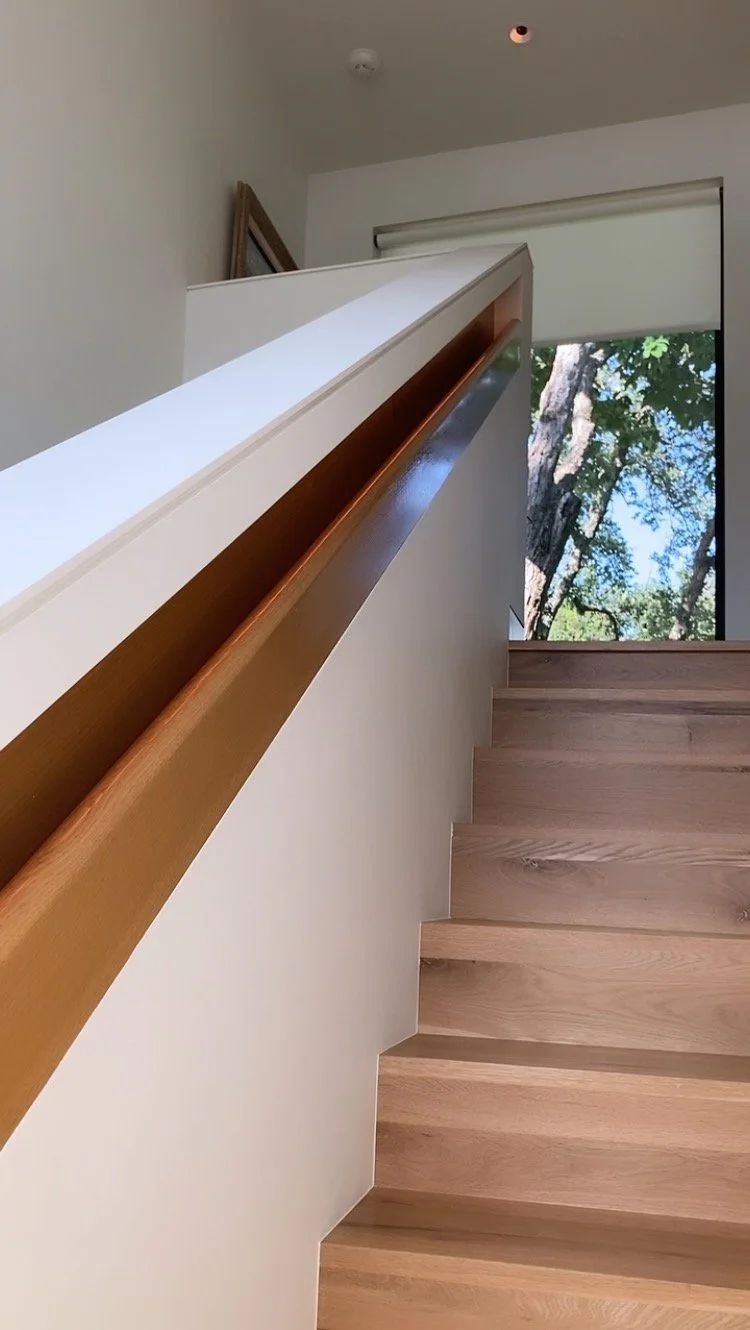
Architectural theory refers to the study and exploration of the underlying principles, concepts, and ideas that inform and guide architectural practice. It is an important tool for understanding and evaluating the role and impact of architecture in society, and for advancing the practice of architecture towards more socially responsible, sustainable, and innovative outcomes.
Building codes are a set of regulations and standards that specify the minimum requirements for the construction, design, and maintenance of buildings. These codes are developed and enforced by local, state, or national governments, and they vary depending on the region and the type of building.
Compliance with building codes is mandatory for all new construction, as well as for renovations and alterations to existing buildings. Building codes are an important tool for protecting public health and safety, and ensuring that buildings are built and maintained to a minimum standard of quality.
Smart home automation refers to the use of technology to automate and control various home appliances and systems, such as lighting, heating, air conditioning, security, entertainment, and more. The aim of smart home automation is to make homes more efficient, comfortable, and convenient, while also providing users with greater control over their home environment.
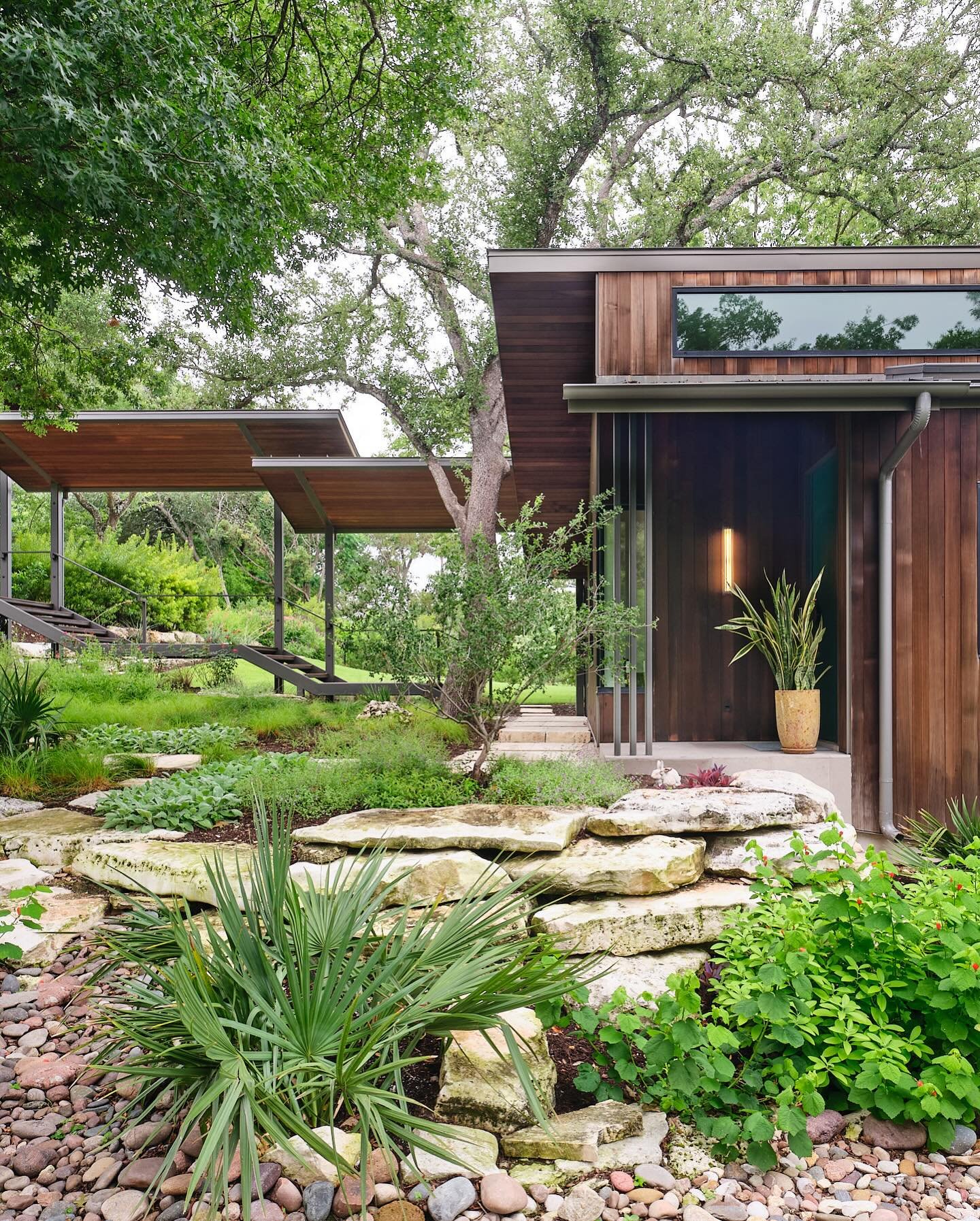
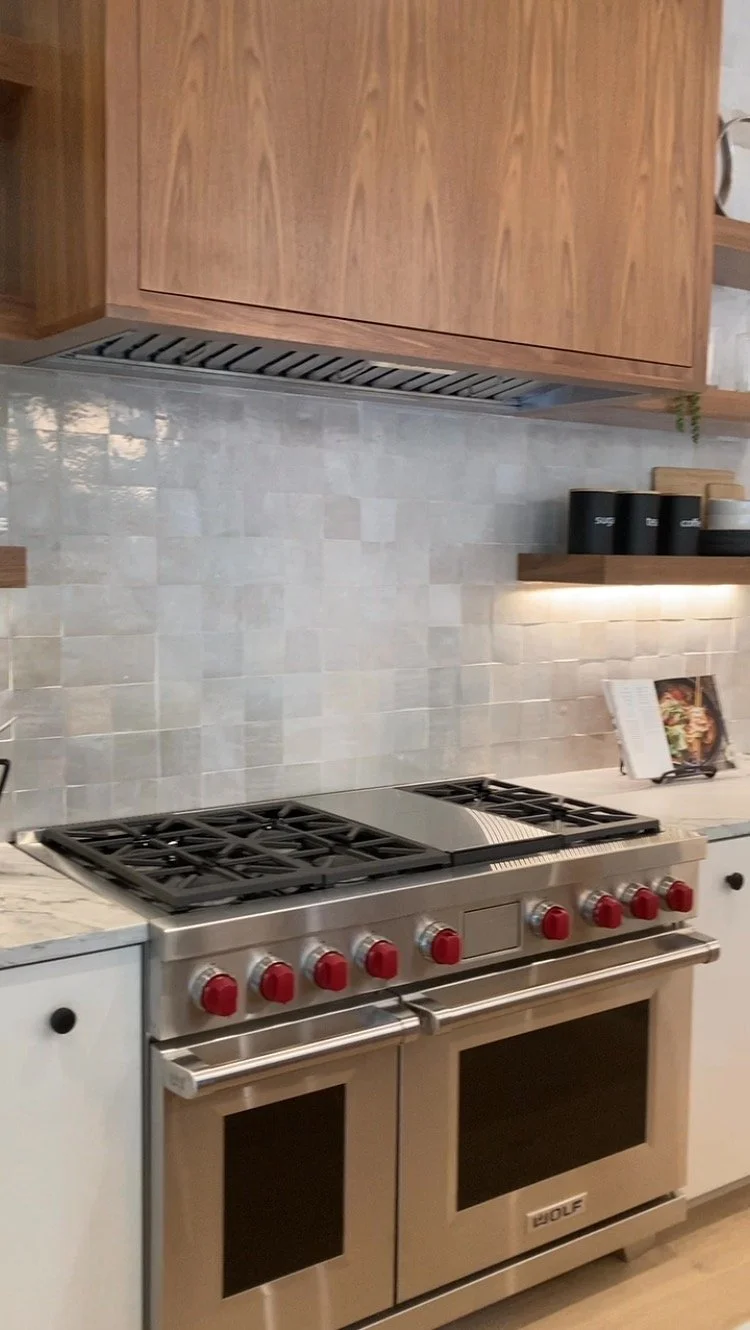
Architecture trends refer to the popular styles, materials, and techniques used in building design and construction. These trends are influenced by a variety of factors, including cultural and social changes, technological advancements, environmental concerns, and economic conditions.
The main goal of BIM is to improve the design, construction, and management of buildings and infrastructure projects by enabling better collaboration, coordination, and communication among all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners. BIM can help reduce errors and rework, enhance productivity, and increase efficiency throughout the life cycle of a project.
Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZs) are a program created by the U.S. government in 2017 under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act to encourage economic development and job creation in economically distressed areas. The QOZ program is intended to attract private investment into low-income communities in order to help revitalize them and create jobs. The program is administered by the U.S. Department of the Treasury and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
The term "Gothic architecture" refers to a style of architecture that emerged in Europe in the 12th century and continued until the 16th century. It is characterized by a number of innovative design features and construction techniques, which allowed builders to create structures that were taller, lighter, and more intricate than ever before.
Land zoning is an essential part of city planning and development, and the City of Austin has a comprehensive Land Development Code (LDC) that regulates land use and development. The LDC divides the city into different zones, each with its own set of regulations and restrictions. The purpose of land zoning in Austin, Texas is to ensure that the city's land is used in a responsible and sustainable manner, and to help create a livable and vibrant community for all of its residents.
Bautex blocks can be used for a variety of construction projects, including residential and commercial buildings, as well as for disaster-resistant structures. They are often used in areas prone to severe weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods.
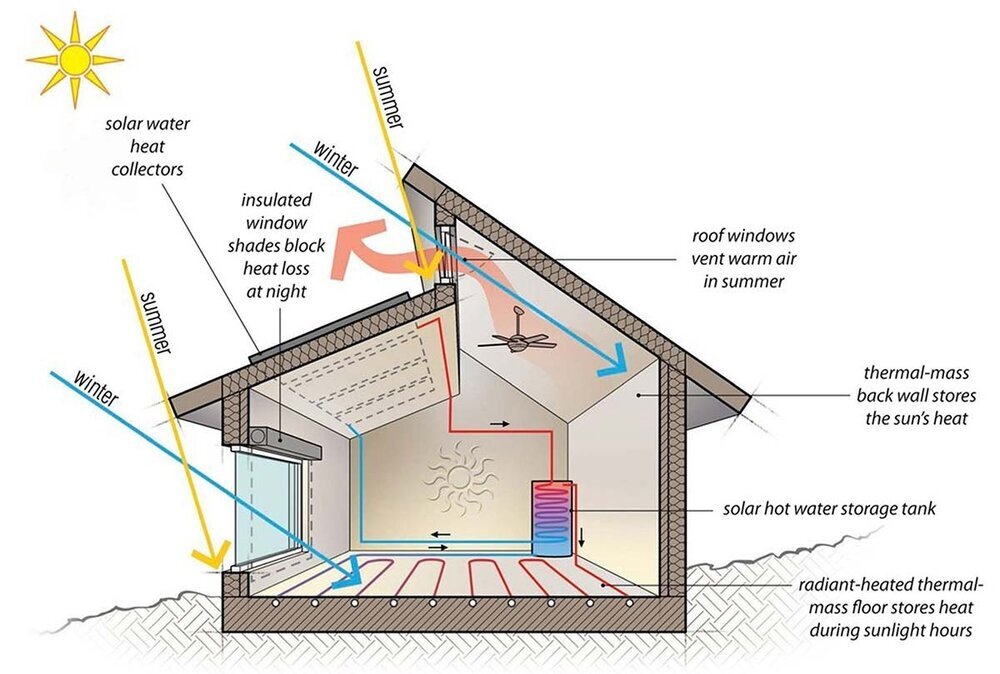
Passive solar design is a set of building techniques that maximize the use of natural energy from the sun to heat, cool, and light a building without the use of mechanical or electrical systems. The principles of passive solar design are adaptable and relevant across a diverse array of building types, encompassing residences, office spaces, educational institutions, and industrial structures.
Shou sugi ban, also known as Yakisugi, is a traditional Japanese technique for preserving wood. The process involves charring the surface of the wood using fire, cooling it down, and then brushing or washing off the excess charred material. This results in a unique, weather-resistant finish that has gained popularity in modern architecture and design. Shou sugi ban can be used for various applications, such as siding, flooring, and furniture, and can be applied to different types of wood, including cedar, cypress, and pine.
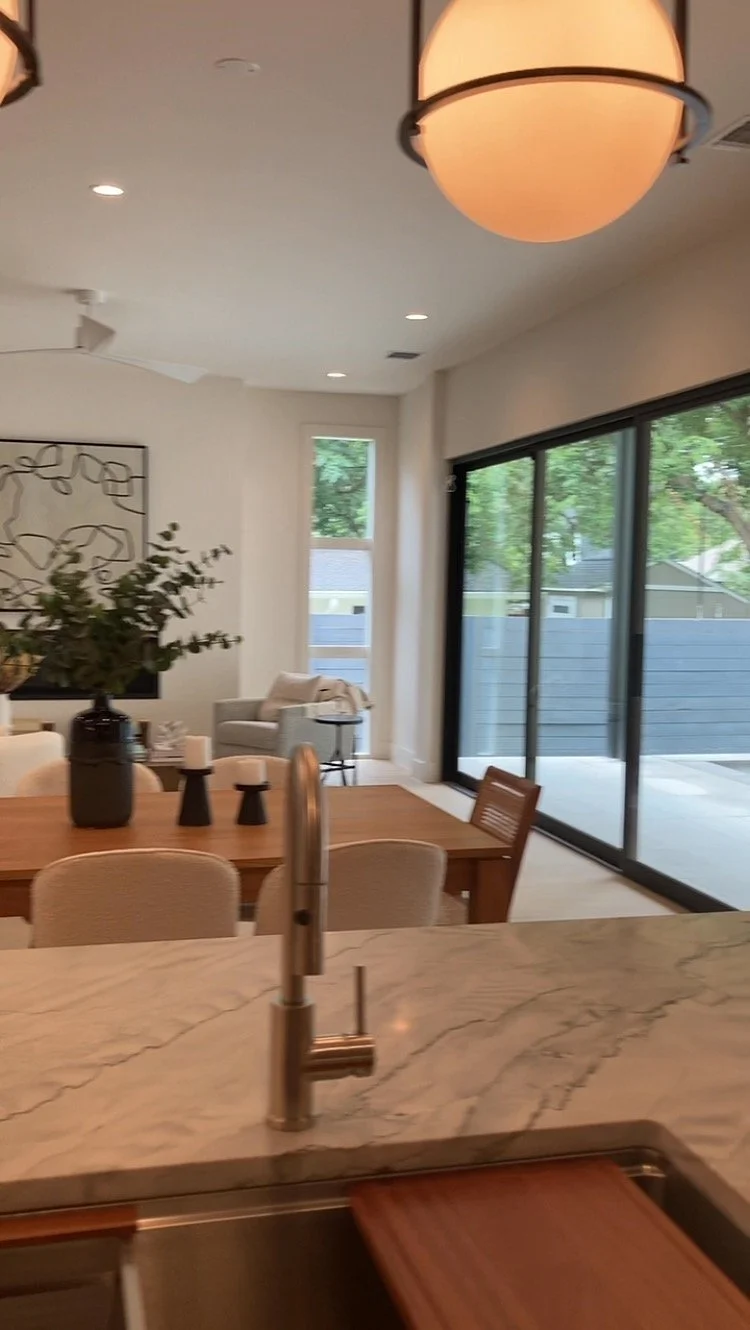
Lighting design is a crucial aspect of architecture, as it has a significant impact on the overall look and feel of a space. Lighting design plays a critical role in architecture, not only in terms of aesthetics but also in terms of functionality, energy efficiency, safety and security, and health and well-being.
Floor Area Ratio (FAR), also known as Floor Space Index (FSI) or Floor Space Ratio, is a planning and zoning regulation that governs the relationship between the total floor area of a building or buildings on a lot and the total area of that lot. FAR is typically expressed as a ratio, representing the total allowable floor area of all buildings on a lot divided by the total area of the lot itself. It is used by local governments and planning authorities to control the density and intensity of development within a specific area.
Rammed earth is a sustainable construction technique that involves compacting a mixture of earth, gravel, sand, silt, and sometimes a small amount of cement or stabilizer, into solid forms to create load-bearing walls and structures. It's an ancient building method that has been used for centuries in various parts of the world.
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the quality of the air inside a building or enclosed space, such as a home, office, or school. The quality of indoor air is important because people spend a significant amount of time indoors, and poor indoor air quality can have negative effects on health and well-being.
Pervious pavers, also known as permeable pavers or porous pavers, are an innovative alternative to traditional pavement materials. They are designed to allow water to pass through the surface into the ground beneath, instead of contributing to stormwater runoff. They can help to improve drainage, reduce stormwater runoff, recharge groundwater supplies, and enhance thermal performance. Additionally, they can provide habitat for plants and animals, which can help to improve biodiversity in urban areas.
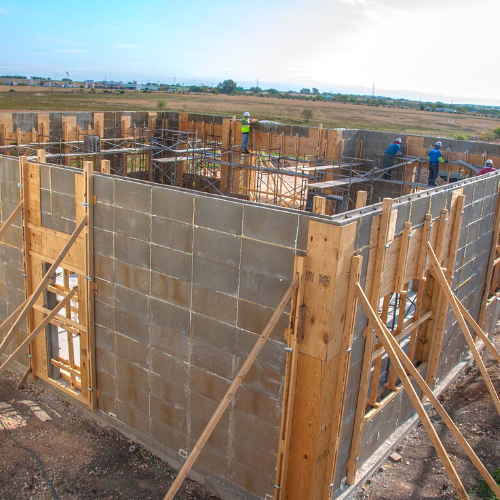
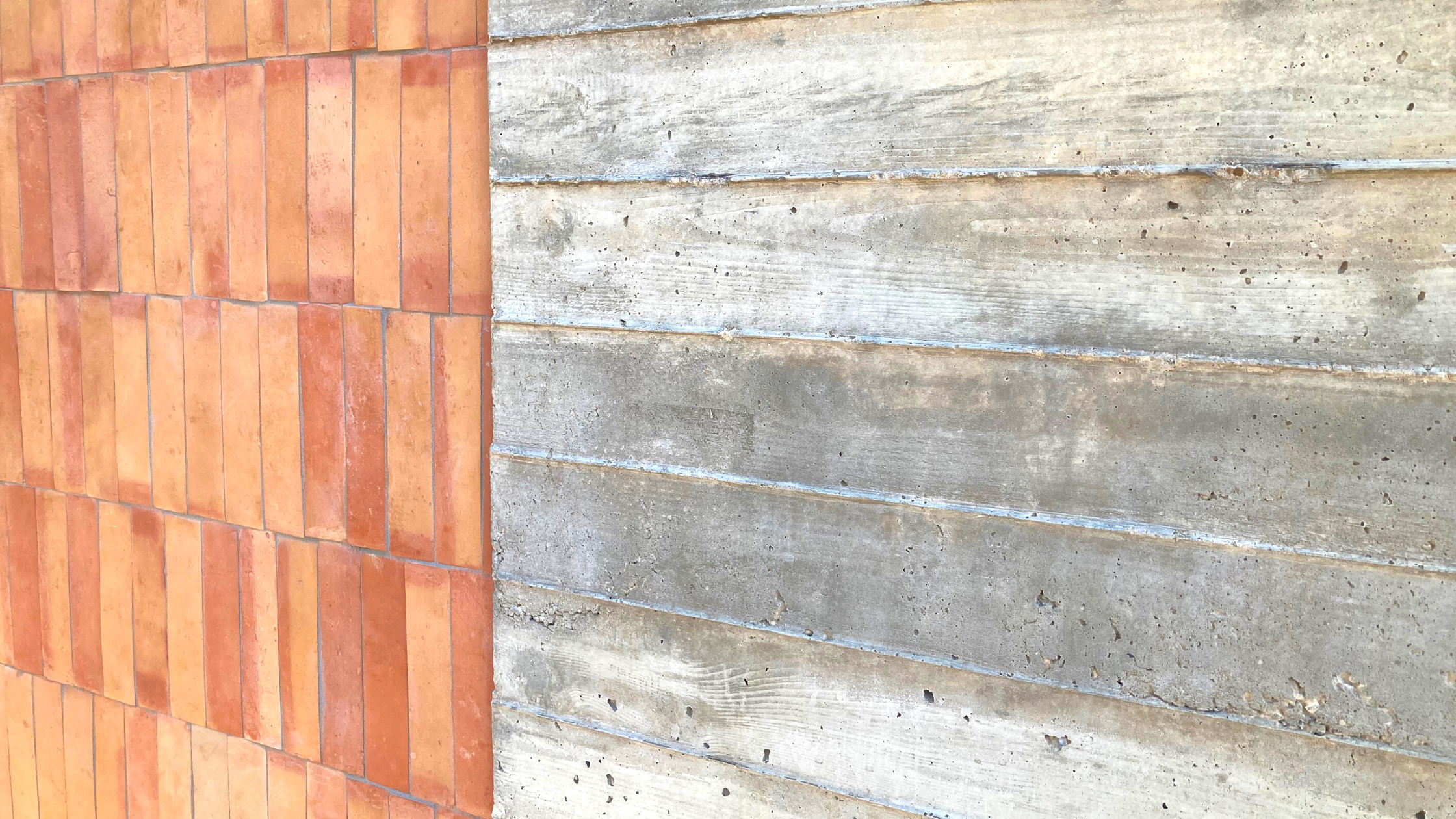
In the realm of architecture, the diverse types of concrete provide architects with a broad range of materials to create enduring and captivating structures. The ongoing development and exploration of concrete technology promise even more innovative applications in the construction industry, shaping the future of architectural design.
A concrete finish refers to the final texture, pattern, or appearance that is applied to a concrete surface to improve its aesthetic appeal and durability. There are various types of concrete finishes that can be used depending on the desired look and function of the concrete surface.
Follow us on social media for more project updates and thoughts about architecture!
Follow us on social media for more project updates and thoughts about architecture!